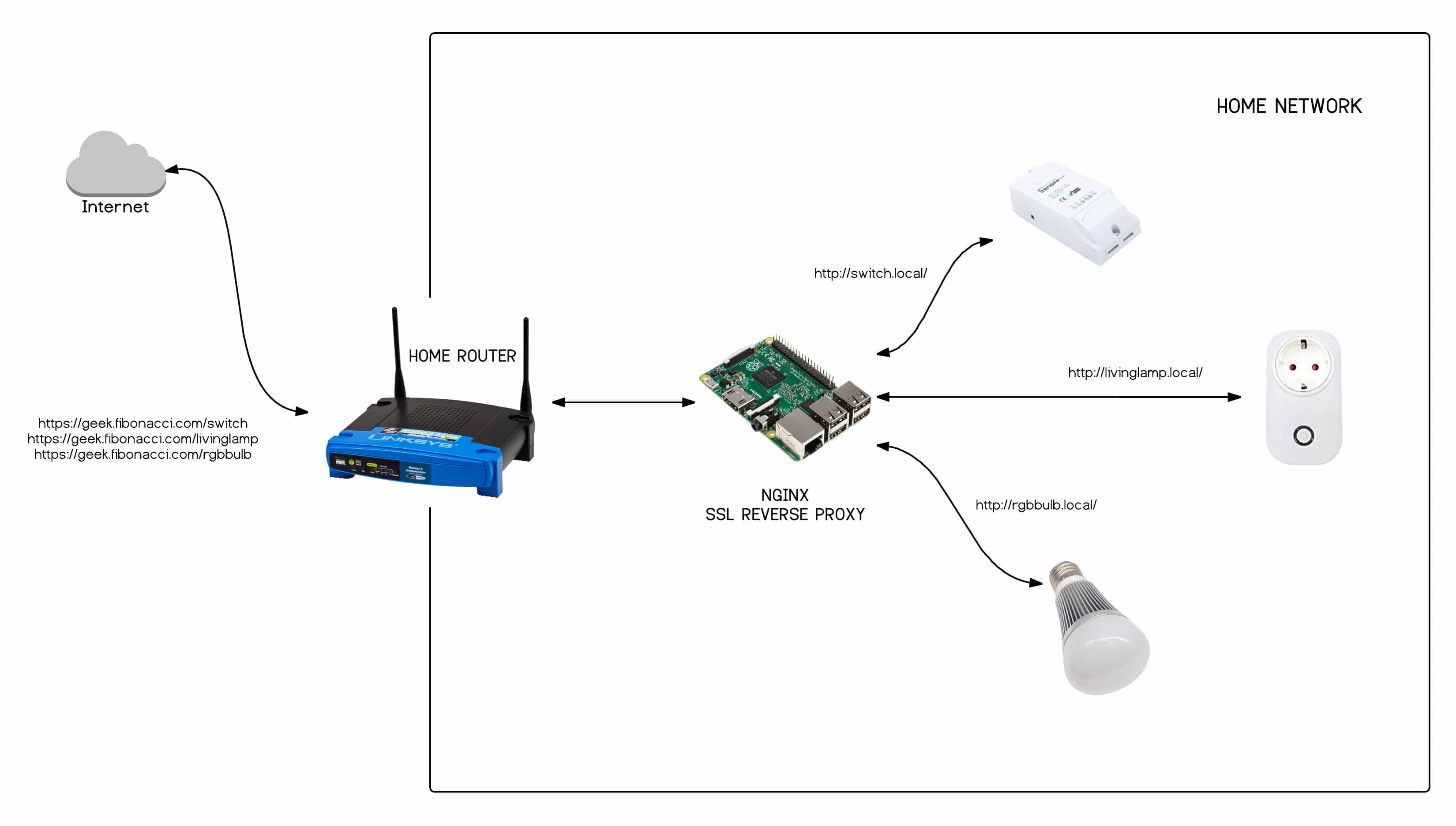
Are you struggling to access your IoT devices remotely while they are behind a router? You're not alone. Many users face challenges when trying to manage IoT devices without relying on MAC addresses. This guide will walk you through the process of setting up remote access for your IoT devices in a secure and efficient manner. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or someone managing smart home devices, understanding how to bypass router restrictions without MAC dependencies is crucial. This article will provide you with step-by-step instructions, practical tips, and expert advice to ensure seamless connectivity.
Remote IoT management is becoming increasingly important in today's interconnected world. From smart thermostats to industrial sensors, IoT devices are transforming how we interact with technology. However, accessing these devices remotely can be tricky, especially when they are hidden behind a router. Without proper configuration, your IoT devices may remain inaccessible, limiting their functionality. This guide will help you overcome these hurdles while adhering to security best practices.
In this article, we will explore various methods to enable remote access to IoT devices without relying on MAC addresses. We'll cover everything from port forwarding and dynamic DNS to advanced techniques like VPNs and cloud-based solutions. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of how to configure your network and devices for remote access, ensuring both convenience and security. Let’s dive in!
Read also:Descendants Of The Sun A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Kdrama
Table of Contents
- Understanding IoT and Remote Access
- Challenges of Accessing IoT Devices Behind a Router
- Methods for Remote Access Without MAC Address
- Port Forwarding for Remote IoT Access
- Dynamic DNS for IoT Devices
- Using VPNs for Secure Remote Access
- Cloud-Based Solutions for IoT Remote Access
- Best Practices for Securing Remote IoT Devices
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding IoT and Remote Access
IoT, or the Internet of Things, refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices range from consumer products like smart speakers and security cameras to industrial equipment and healthcare devices. Remote access to IoT devices allows users to monitor, control, and manage these devices from anywhere in the world, provided they have an internet connection.
Remote access is essential for maximizing the functionality of IoT devices. For instance, a smart thermostat can be adjusted remotely to save energy, or a security camera can be monitored in real-time to ensure safety. However, achieving seamless remote access requires proper configuration of both the IoT device and the network infrastructure, particularly when the device is located behind a router.
Why Remote Access Matters
- Enables real-time monitoring and control of IoT devices.
- Improves efficiency by allowing users to manage devices from anywhere.
- Enhances security by providing remote access to surveillance systems.
Challenges of Accessing IoT Devices Behind a Router
When IoT devices are placed behind a router, they are often assigned private IP addresses that are not directly accessible from the internet. This creates a barrier for remote access, as external devices cannot communicate with the IoT device without proper configuration. Additionally, many routers use Network Address Translation (NAT), which further complicates direct communication.
Another challenge is the lack of reliance on MAC addresses. While MAC addresses are unique identifiers for devices on a local network, they are not routable over the internet. This means that remote access solutions must rely on other methods to identify and connect to IoT devices.
Common Issues
- Private IP addresses are not reachable from the internet.
- NAT prevents direct communication between external and internal devices.
- MAC addresses cannot be used for remote identification.
Methods for Remote Access Without MAC Address
Fortunately, there are several methods to enable remote access to IoT devices without relying on MAC addresses. These methods include port forwarding, dynamic DNS, VPNs, and cloud-based solutions. Each approach has its own advantages and considerations, which we will explore in detail.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a technique that allows external devices to access a specific device on a local network by forwarding traffic from a specific port on the router to the device's private IP address. This method is widely used for remote access but requires careful configuration to avoid security risks.
Read also:Understanding Enough Hi A Comprehensive Guide To Finding Balance And Contentment
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a service that maps a domain name to a changing IP address. This is particularly useful for users with dynamic IP addresses provided by their internet service provider (ISP). By using DDNS, you can access your IoT devices remotely using a domain name instead of an IP address.
Port Forwarding for Remote IoT Access
Port forwarding is one of the most common methods for enabling remote access to IoT devices. It involves configuring your router to forward incoming traffic on a specific port to the private IP address of the IoT device. Here's how you can set it up:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Access your router's admin panel by entering its IP address in a web browser.
- Navigate to the port forwarding section, often found under "Advanced Settings" or "NAT."
- Create a new port forwarding rule by specifying the external port, internal IP address, and internal port of the IoT device.
- Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
Security Considerations
- Use non-standard ports to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Enable firewall rules to restrict access to trusted IP addresses.
- Regularly update your router's firmware to patch security vulnerabilities.
Dynamic DNS for IoT Devices
Dynamic DNS is an excellent solution for users with dynamic IP addresses. It allows you to assign a domain name to your IoT device, making it easier to access remotely. Many DDNS services are available for free or at a low cost, and they integrate seamlessly with most routers.
Setting Up Dynamic DNS
- Choose a DDNS provider, such as No-IP or DuckDNS.
- Create an account and register a domain name.
- Configure your router to update the DDNS service with your current IP address.
- Access your IoT device using the domain name instead of the IP address.
Benefits of Dynamic DNS
- Eliminates the need to remember or track changing IP addresses.
- Works seamlessly with most routers and IoT devices.
- Provides a user-friendly way to access devices remotely.
Using VPNs for Secure Remote Access
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure way to access your IoT devices remotely. By connecting to your home network through a VPN, you can bypass the need for port forwarding or DDNS while ensuring encrypted communication.
How VPNs Work
VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and your home network. Once connected, you can access your IoT devices as if you were on the local network. This method is particularly useful for users who prioritize security and privacy.
Setting Up a VPN
- Choose a VPN solution, such as OpenVPN or WireGuard.
- Install and configure the VPN server on your router or a dedicated device.
- Download the VPN client on your remote device and connect to the server.
- Access your IoT devices securely through the VPN connection.
Cloud-Based Solutions for IoT Remote Access
Cloud-based solutions offer a convenient and scalable way to manage IoT devices remotely. Many IoT platforms provide built-in cloud services that allow users to access their devices through a web interface or mobile app.
Advantages of Cloud-Based Solutions
- No need for complex network configurations.
- Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Often includes additional features like analytics and automation.
Popular Cloud Platforms
- AWS IoT Core
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub
- Google Cloud IoT
Best Practices for Securing Remote IoT Devices
Security is a critical consideration when enabling remote access to IoT devices. Without proper safeguards, your devices could be vulnerable to cyberattacks, leading to data breaches or unauthorized control.
Security Tips
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While setting up remote access for IoT devices, it's easy to make mistakes that could compromise security or functionality. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
Mistakes to Avoid
- Using default passwords for IoT devices and routers.
- Leaving unnecessary ports open on your router.
- Ignoring firmware updates and security patches.
- Failing to encrypt communication between devices.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In this guide, we've explored various methods for enabling remote access to IoT devices behind a router without relying on MAC addresses. From port forwarding and dynamic DNS to VPNs and cloud-based solutions, there are multiple approaches to suit different needs and preferences. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure seamless and secure remote access to your IoT devices.
Remember to prioritize security by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping your devices updated. Avoid common mistakes like leaving ports open or ignoring firmware updates. If you found this guide helpful, consider sharing it with others or leaving a comment below. For more tips and tutorials, explore our other articles on IoT and networking.