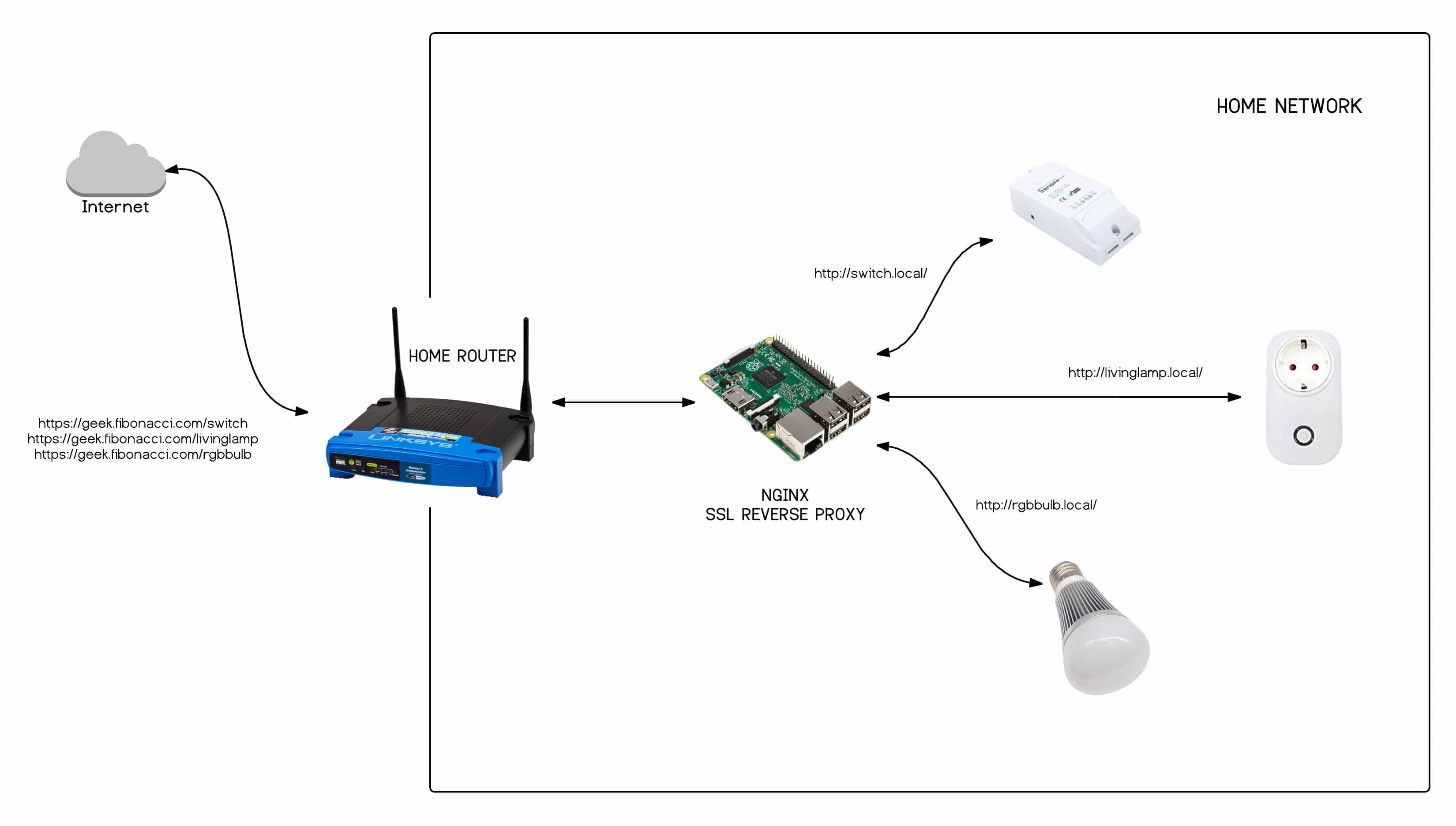
Are you struggling to connect your IoT devices remotely behind a router with MAC address filtering? You're not alone. Many users face challenges when trying to access their IoT devices from outside their local network, especially when MAC address restrictions are in place. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about overcoming these hurdles and ensuring seamless remote access to your IoT devices. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or a beginner, this article will provide clear, actionable steps to help you succeed.
Remote IoT access is becoming increasingly essential as smart homes, businesses, and industries rely on connected devices for automation, monitoring, and control. However, the combination of router-level MAC filtering and IoT device connectivity can create barriers that seem difficult to overcome. In this article, we’ll explore how to bypass these restrictions while maintaining security and efficiency.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a thorough understanding of how to configure your router, IoT devices, and network settings to enable remote access. We’ll also cover important considerations like security risks, best practices, and troubleshooting tips to ensure your setup is both functional and safe. Let’s dive into the details and unlock the full potential of your IoT ecosystem.
Read also:Vegamovies Nl Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Movies Online
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote IoT Access
- Understanding MAC Address Filtering
- Challenges of Using IoT Devices Behind a Router
- Step-by-Step Guide to Enable Remote Access
- Configuring Your Router for Remote IoT
- Advanced Techniques for Remote IoT Access
- Security Best Practices
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Tools and Resources for Remote IoT Management
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Remote IoT Access
Remote IoT access refers to the ability to interact with and control IoT devices from a location outside your local network. This capability is crucial for managing smart home devices, industrial sensors, or any connected system that requires monitoring or adjustments from afar. However, achieving reliable remote access often involves navigating complex network configurations, including router settings like MAC address filtering.
IoT devices communicate over the internet using IP addresses, but routers often employ additional layers of security, such as MAC address filtering, to restrict unauthorized access. While this enhances security, it can also complicate remote access unless properly configured. Understanding the basics of IoT connectivity and how routers manage network traffic is the first step toward solving these challenges.
Understanding MAC Address Filtering
MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering is a security feature used by routers to allow or deny network access based on the unique hardware identifier of each device. Every network-enabled device, including IoT gadgets, has a MAC address assigned by its manufacturer. By enabling MAC filtering, you can create a whitelist or blacklist of devices that are permitted or blocked from connecting to your network.
While MAC filtering adds an extra layer of protection, it can pose challenges for remote IoT access. For instance, if your IoT device is behind a router with MAC filtering enabled, it may not be able to communicate with external servers unless specific configurations are made. This section will delve deeper into how MAC filtering works and its implications for IoT connectivity.
How MAC Filtering Works
MAC filtering operates at the data link layer of the OSI model. When a device attempts to connect to a network, the router checks its MAC address against a predefined list. If the address is on the whitelist, the device gains access; otherwise, it is denied. This process occurs before IP-based communication begins, making it a powerful tool for network administrators.
- Whitelist: Only devices with approved MAC addresses can connect.
- Blacklist: Devices with blocked MAC addresses are denied access.
Challenges of Using IoT Devices Behind a Router
Using IoT devices behind a router with MAC filtering can present several challenges. These include limited accessibility, increased complexity in configuration, and potential security vulnerabilities. Let’s explore these challenges in detail.
Read also:Bridge To Terabithia A Timeless Journey Of Friendship Imagination And Growth
Limited Accessibility
One of the primary issues is that IoT devices behind a router with MAC filtering may not be reachable from external networks. This limitation can prevent users from remotely controlling or monitoring their devices, which defeats the purpose of having smart technology.
Increased Configuration Complexity
Configuring a router to allow remote access while maintaining MAC filtering requires technical expertise. Users must understand how to whitelist IoT devices, set up port forwarding, and configure dynamic DNS services. These steps can be daunting for non-technical users.
Security Vulnerabilities
While MAC filtering enhances security, it is not foolproof. Determined attackers can spoof MAC addresses to bypass filters. Additionally, opening ports for remote access can expose your network to potential threats if not properly secured.
Step-by-Step Guide to Enable Remote Access
Now that we’ve discussed the challenges, let’s move on to a practical solution. Below is a step-by-step guide to enabling remote IoT access behind a router with MAC filtering.
Step 1: Identify Your IoT Device’s MAC Address
The first step is to locate the MAC address of your IoT device. This information is usually available in the device’s settings menu or documentation. Once identified, note it down for future reference.
Step 2: Access Your Router’s Admin Panel
Log in to your router’s admin panel using its IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Enter your credentials to access the settings page.
Step 3: Enable MAC Address Whitelisting
Navigate to the MAC filtering section of your router’s settings. Add the MAC address of your IoT device to the whitelist to ensure it can connect to the network.
Step 4: Set Up Port Forwarding
Configure port forwarding to direct incoming traffic to your IoT device. Assign a specific port number and map it to the device’s local IP address.
Step 5: Configure Dynamic DNS
If your ISP assigns a dynamic public IP address, set up a dynamic DNS service to maintain a consistent domain name for remote access.
Configuring Your Router for Remote IoT
Proper router configuration is critical for enabling remote IoT access. This section will cover advanced router settings, including firewall rules, VLANs, and Quality of Service (QoS).
Firewall Rules
Adjust your router’s firewall settings to allow traffic on the ports used by your IoT device. Be cautious not to open unnecessary ports, as this could expose your network to risks.
VLANs for Network Segmentation
Use VLANs to segment your network and isolate IoT devices from other devices. This approach enhances security by limiting cross-device communication.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Enable QoS to prioritize traffic for your IoT devices, ensuring they receive sufficient bandwidth for optimal performance.
Advanced Techniques for Remote IoT Access
For users seeking more advanced solutions, techniques like reverse SSH tunneling and VPNs can provide secure and reliable remote access.
Reverse SSH Tunneling
Reverse SSH tunneling allows you to create a secure connection between your IoT device and an external server. This method bypasses the need for port forwarding and is highly secure.
Using a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts all traffic between your IoT device and remote client, ensuring privacy and security. Many routers support VPN configurations, making this a viable option for advanced users.
Security Best Practices
When enabling remote IoT access, security should be a top priority. Follow these best practices to protect your network and devices.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enable encryption protocols like WPA3 for Wi-Fi networks.
- Monitor network activity for unusual behavior.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful configuration, issues may arise. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
Device Not Connecting
Ensure the MAC address is correctly whitelisted and that the device is powered on. Double-check the router’s settings for typos or errors.
Port Forwarding Not Working
Verify that the correct port number is assigned and that no conflicting rules exist in the router’s configuration.
Dynamic DNS Issues
Check your dynamic DNS service provider for outages or misconfigurations. Ensure the client software is running on your router or computer.
Tools and Resources for Remote IoT Management
Several tools and platforms can simplify remote IoT management. These include:
- No-IP: A popular dynamic DNS service.
- OpenVPN: An open-source VPN solution.
- Home Assistant: A platform for managing smart home devices.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Enabling remote IoT access behind a router with MAC filtering is achievable with the right configuration and tools. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can overcome connectivity challenges and unlock the full potential of your IoT ecosystem. Remember to prioritize security and regularly update your devices to mitigate risks.
If you found this guide helpful, please share it with others who might benefit. Leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions, and explore our other articles for more insights into IoT and networking. Together, let’s build a smarter, more connected world!