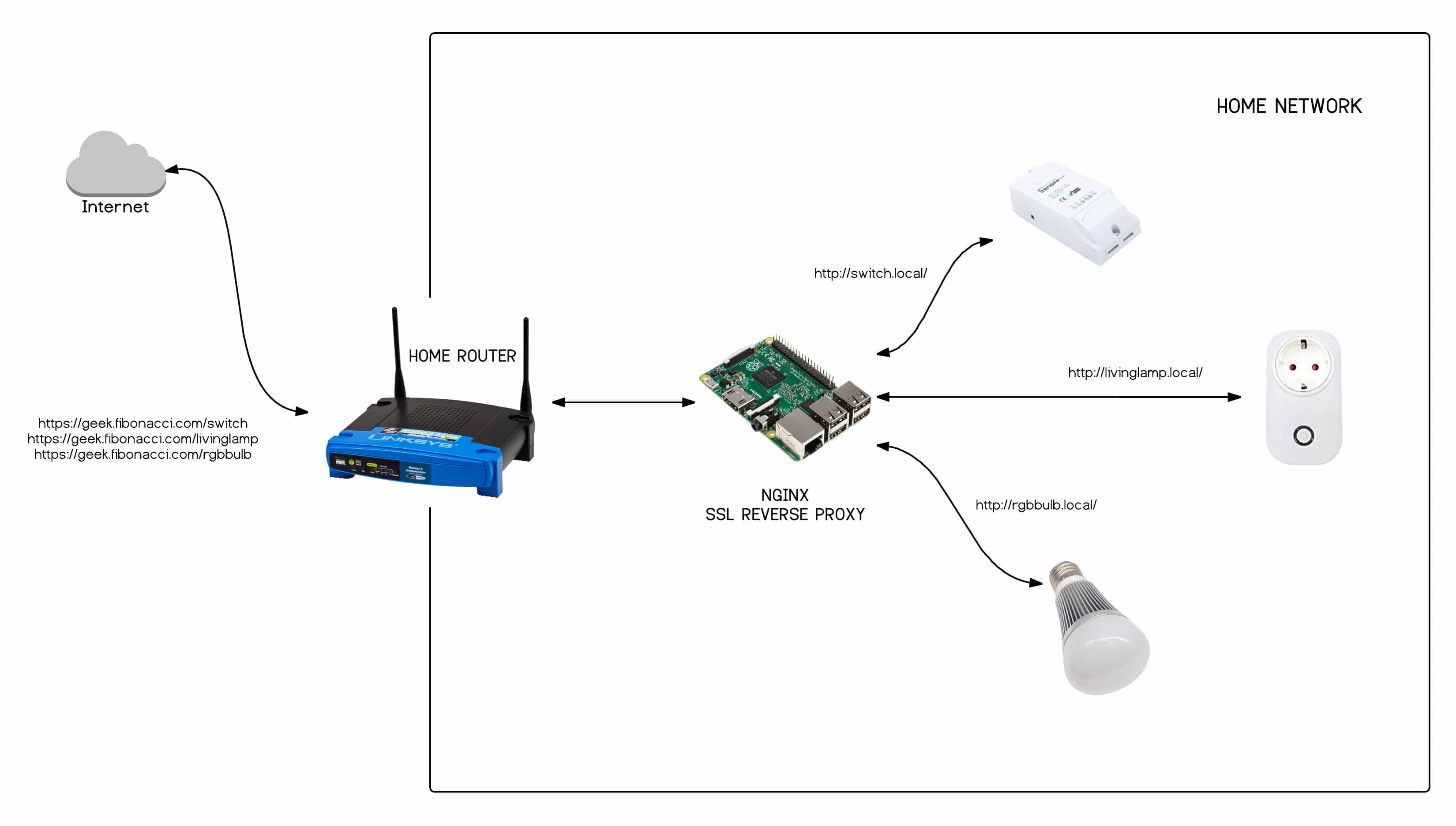
Managing IoT devices remotely can be a challenge, especially when they are located behind a router with MAC address restrictions. However, with the right strategies and tools, you can overcome these limitations and ensure seamless connectivity for your IoT devices. Whether you're managing smart home devices, industrial sensors, or any IoT-enabled technology, understanding how to bypass MAC restrictions is crucial for uninterrupted operation. In this article, we will explore step-by-step methods to achieve this, ensuring your IoT devices remain accessible and functional from anywhere in the world.
Remote IoT management is becoming increasingly important as the Internet of Things continues to expand. With the growing number of connected devices, ensuring secure and reliable access is paramount. Many users face challenges when trying to access their IoT devices remotely, especially when routers impose MAC address restrictions. These restrictions can limit device connectivity and create barriers to seamless remote management. Fortunately, there are ways to navigate these challenges effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various techniques and tools that allow you to use remote IoT devices behind a router without MAC restrictions. From port forwarding to using virtual private networks (VPNs) and cloud-based solutions, we will cover everything you need to know. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to manage your IoT devices remotely, ensuring they remain accessible and secure.
Read also:Unraveling The Legacy Of Hulk Hogan The Icon Who Redefined Wrestling
Table of Contents
- Understanding IoT and MAC Restrictions
- Challenges of Remote IoT Management
- Port Forwarding for Remote Access
- Using VPN for Secure Connections
- Cloud-Based IoT Management Solutions
- Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
- Tools and Software for Remote IoT
- Best Practices for Remote IoT Security
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding IoT and MAC Restrictions
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices range from smart home appliances to industrial sensors and healthcare equipment. One common challenge in managing IoT devices is dealing with MAC address restrictions imposed by routers. A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communication on a network. Some routers allow only specific MAC addresses to connect, which can limit the accessibility of IoT devices.
MAC restrictions are often implemented for security reasons, as they help prevent unauthorized devices from accessing a network. However, these restrictions can create barriers when trying to manage IoT devices remotely. For instance, if your IoT device is located behind a router with MAC filtering enabled, you may face difficulties accessing it from an external network. Understanding how MAC restrictions work is the first step in overcoming these limitations.
Challenges of Remote IoT Management
Managing IoT devices remotely presents several challenges, especially when dealing with network restrictions. One of the primary challenges is ensuring secure and reliable access to devices located behind a router. MAC address restrictions can complicate this process, as they limit which devices can connect to the network. Additionally, dynamic IP addresses assigned by internet service providers (ISPs) can make it difficult to maintain a consistent connection to IoT devices.
Another challenge is ensuring the privacy and security of data transmitted between IoT devices and remote users. Without proper security measures, sensitive information could be intercepted or compromised. Furthermore, managing multiple IoT devices across different locations can be cumbersome, requiring robust tools and strategies to streamline the process.
Port Forwarding for Remote Access
Port forwarding is a technique that allows external devices to access services on a private network by redirecting incoming network traffic to a specific device. This method can be particularly useful for accessing IoT devices behind a router with MAC restrictions. By configuring port forwarding rules on your router, you can ensure that external requests are routed to the correct IoT device.
To set up port forwarding, follow these steps:
Read also:Barbara Billingsley The Iconic Mother Figure Of American Television
- Access your router's admin panel by entering its IP address in a web browser.
- Navigate to the port forwarding section, often found under "Advanced Settings" or "NAT."
- Create a new port forwarding rule by specifying the external port, internal IP address, and internal port of the IoT device.
- Save the settings and test the connection to ensure it works.
While port forwarding is effective, it is essential to consider the security implications. Open ports can expose your network to potential threats, so it is crucial to implement strong firewall rules and use secure protocols such as HTTPS.
Benefits of Port Forwarding
Port forwarding offers several advantages for remote IoT management:
- Enables direct access to IoT devices without requiring MAC address whitelisting.
- Improves connectivity and reduces latency for remote operations.
- Can be configured for multiple devices, allowing simultaneous access.
Using VPN for Secure Connections
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is another effective solution for accessing IoT devices behind a router with MAC restrictions. A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the network, allowing you to bypass MAC filtering and access IoT devices remotely. By connecting to a VPN server located on the same network as your IoT devices, you can effectively bypass router restrictions.
To set up a VPN for remote IoT access:
- Choose a reliable VPN service or set up your own VPN server using software like OpenVPN or WireGuard.
- Configure the VPN server to allow access to the local network where your IoT devices are located.
- Install the VPN client on your remote device and connect to the VPN server.
- Access your IoT devices as if you were on the local network.
Using a VPN not only bypasses MAC restrictions but also enhances security by encrypting all data transmitted between your device and the network. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected from potential threats.
Advantages of Using a VPN
Here are some benefits of using a VPN for remote IoT management:
- Provides a secure and encrypted connection to IoT devices.
- Bypasses MAC address restrictions imposed by routers.
- Allows access to multiple devices on the same network simultaneously.
Cloud-Based IoT Management Solutions
Cloud-based IoT management platforms offer a convenient and scalable solution for accessing IoT devices remotely. These platforms provide a centralized interface for managing multiple devices, regardless of their location or network restrictions. By connecting your IoT devices to a cloud platform, you can access them from anywhere in the world without worrying about MAC address restrictions.
Popular cloud-based IoT platforms include AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Google Cloud IoT. These platforms offer features such as device monitoring, data analytics, and remote control, making it easier to manage IoT devices efficiently. Additionally, they provide built-in security measures to protect your devices and data from unauthorized access.
To use a cloud-based solution, follow these steps:
- Choose a cloud IoT platform that suits your needs.
- Register your IoT devices with the platform and configure their settings.
- Install the necessary software or firmware on your devices to enable cloud connectivity.
- Access and manage your devices through the platform's web interface or mobile app.
Why Choose Cloud-Based Solutions?
Cloud-based IoT management solutions offer several advantages:
- Eliminate the need for complex network configurations, such as port forwarding or VPN setup.
- Provide real-time monitoring and analytics for better decision-making.
- Offer scalability to accommodate growing numbers of IoT devices.
Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a service that maps a dynamic IP address to a static domain name, allowing you to access IoT devices remotely even if your ISP assigns a changing IP address. This is particularly useful for users who do not have a static IP address and need a consistent way to connect to their IoT devices.
To set up DDNS:
- Sign up for a DDNS service provider, such as No-IP or DynDNS.
- Create a hostname and link it to your dynamic IP address.
- Configure your router or IoT device to update the DDNS service whenever your IP address changes.
- Use the hostname to access your IoT devices remotely.
Dynamic DNS is a cost-effective and straightforward solution for remote IoT management, especially for users with limited technical expertise.
Tools and Software for Remote IoT
Several tools and software solutions are available to simplify remote IoT management. These tools provide features such as device monitoring, automation, and secure access, making it easier to manage IoT devices behind a router with MAC restrictions.
Some popular tools include:
- Home Assistant: An open-source platform for managing smart home devices.
- Node-RED: A visual programming tool for automating IoT workflows.
- MQTT: A lightweight messaging protocol for IoT communication.
These tools can be integrated with cloud platforms or used independently to enhance remote IoT management capabilities.
Best Practices for Remote IoT Security
Ensuring the security of your IoT devices is critical when managing them remotely. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor network activity for suspicious behavior.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When managing IoT devices remotely, avoid these common mistakes:
- Using default passwords or weak credentials.
- Leaving unnecessary ports open on your router.
- Ignoring firmware updates and security patches.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In this article, we have explored various methods for using remote IoT devices behind a router without MAC restrictions. From port forwarding and VPNs to cloud-based solutions and dynamic DNS, there are multiple strategies to ensure seamless connectivity. By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, you can enhance the security and reliability of your remote IoT management.
We encourage you to try the techniques discussed in this article and share your experiences in the comments below. If you found this guide helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from it. For more tips and resources on IoT management, explore our other articles on the topic.